Build Heterostructure
Splicing the selected 2 or 3 structures sequentially in a certain direction into a structure can generate 1D/2D, 2D/2D, 2D/3D and other types of heterojunctions; It can be selected when the lattice matching method is to keep the volume constant
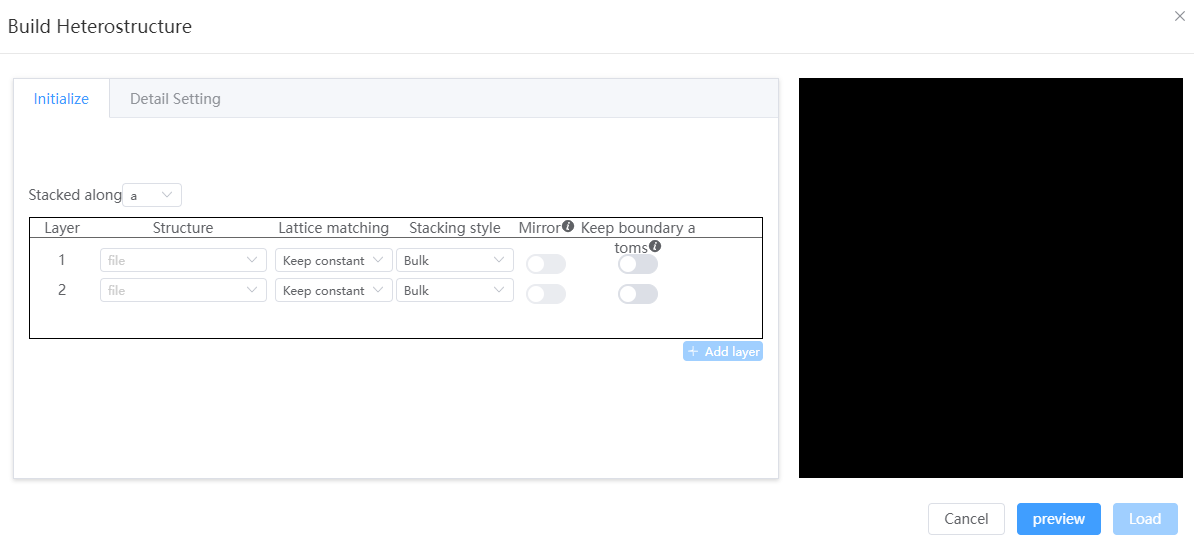
- Initialize
- Stacked along: can be
a,b,c; Stacks structures sequentially by layer in the selected direction - Structure: Currently must be a lattice structure
- Lattice matching: When stitching a structure, the structural lattice is adjusted. You can choose
keep volume constantorkeep thickness constant - Stacking style:
- When the lattice matches
keep volume constant, the stacking method must bevolume materialand the volume (density) of the structure must be unchanged - When the lattice is matched to
keep thickness constant, the stacking method can bebulk material,two-dimensional material,isolated system.Volume materialhas a constant spacing of atomic layers in the structure;Two-dimensional materialsremove the vacuum layer in the stacking direction, while the atomic layer spacing remains unchanged; Theisolated systemremoves all vacuum layers while keeping the atomic spacing unchanged.
- When the lattice matches
- Mirror: The pre-stack structure is mirrored in the stacking direction, requiring the stacking direction to be orthogonal to the other two vector directions. For example, when the stacking direction is
a, β=γ=90° is required, and the structure is mirrored in thebcplane - Keep boundary atoms: Preserve all atoms on the boundary of the structure along the stacking direction. For example, when the stacking direction is
a, all atoms with fractional coordinates (0.0, y, z), (1.0, y, z) are retained.
- Stacked along: can be
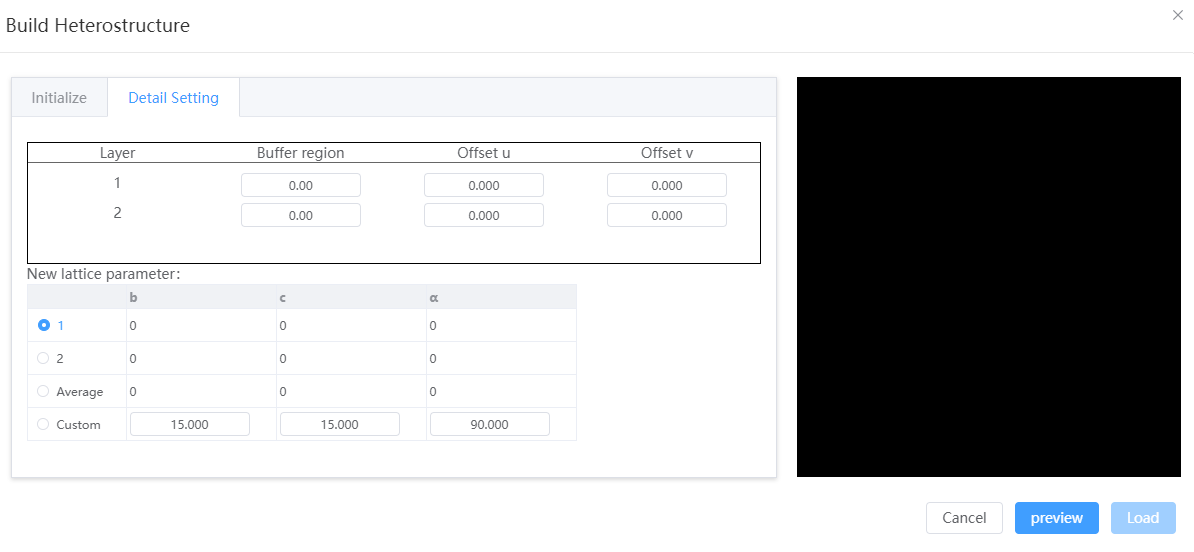
- Detail setting
- Buffer region: After stacking, add a buffer distance (vacuum)
- Offset U, V: Before stacking, all atoms in the structure are translated in the plane of the vertical stacking direction for fractional coordinates
- New lattice parameter: The lattice constant of a heterogeneous structure
- When the stacking direction is
a: the values ofb,c,αneed to be determined,ais calculated,β,γwill be averaged by each structure - When the stacking direction is
b: you need to determine the values ofc,a,β,bis calculated,γ,αwill be averaged by each structure - When the stacking direction is
c: you need to determine the values ofa,b,γ,cis calculated,α,βwill be averaged by each structure
- When the stacking direction is