Molecule Ethylene Carbonate System
The following example, based on an isolated C3H4O3 system, demonstrates how to train and use the PWMLFF Neural Network Model for prediction.
The overall program workflow is roughly divided into:
1. Generating the Dataset
Using the C3H4O3 data obtained from a PWmat AIMD simulation, the data file MOVEMENT contains 200 structures, each consisting of 10 atoms.
Sample etot.input File:
8 1
JOB = MD
MD_DETAIL = 2 200 1 400 400
XCFUNCTIONAL = PBE
Ecut = 60
ECUT2 = 240
MP_N123 = 1 1 1 0 0 0 3
ENERGY_DECOMP = T
OUT.STRESS = F
IN.ATOM = atom.config
IN.PSP1 = C.SG15.PBE.UPF
IN.PSP2 = H.SG15.PBE.UPF
IN.PSP3 = O.SG15.PBE.UPF
- Optional
ENERGY_DECOMP: Whether to decompose the total DFT energy into atomic energies (atomic energy). The results are output in theMOVEMENTfile. To use or train atomic energy, set this toT. - Optional
OUT.STRESS: Whether to output stress information. To trainVirial, set this toT. - Other parameter details can be found in the PWmat manual.
2. Training Process
2.1 Feature Extraction
Create a new directory and place the MOVEMENT* files there. Alternatively, these files can be located in other directories, and you can adjust the train_movement_path in the *.json input file accordingly.
2.2 Training Input File
In the current directory, create a new *.json file (e.g., nn_ec.json). This file will contain a series of required parameters.
Example Input File (Details on Other Parameters):
{
"train_movement_file":["./EC_MOVEMENT"],
"model_type": "NN",
"atom_type":[8,6,1]
}
train_movement_file: Name of theMOVEMENTfile(s). Multiple files can be specified. Adjust according to your setup.model_type: Model type, referring to the model used for training. Other models and parameter configurations are detailed in Parameter Details.atom_type: Specifies the atomic types, where 8, 6, and 1 correspond to O, C, and H atomic numbers, respectively.
2.3 Running the Program
The following slurm script example is suitable for Mcloud. Ensure that the necessary environment and modules are loaded when submitting the job.
#!/bin/sh
#SBATCH --partition=3080ti
#SBATCH --job-name=mlff
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:1
#SBATCH --gpus-per-task=1
#Mcloud installed environment loaded
# Recommended here
source /share/app/PWMLFF/PWMLFF2024.5/env.sh
# Alternatively, the following method can be used for step-by-step loading
# source /share/app/anaconda3/etc/profile.d/conda.sh
# module load conda/3-2020.07
# conda deactivate
# conda activate PWMLFF
# module load pwmlff/2024.5
PWMLFF train nn_ec.json > log
To run interactively:
$ srun -p 3080ti --gres=gpu:1 --pty /bin/bash
$ source /share/app/PWMLFF/PWMLFF2024.5/env.sh
$ PWMLFF train nn_ec.json
Generating features and training can be run separately:
PWMLFF gen_feat nn_ec.json- Only used to generate features.PWMLFF train nn_ec.json- Loads and processes features before starting training. Runningtraindirectly will automatically callgen_feat. Ifgen_feathas already been run, you can set thetrain_feature_pathin the.jsonfile to specify the feature path, and comment outtrain_movement_file.
After running the program, the forcefield and model_record directories will be generated in the execution directory:
EC_system/
└── dir
├── forcefield
│ ├── forcefield.ff
│ ├── fread_dfeat
│ │ ├── data_scaler.txt
│ │ ├── feat.info
│ │ ├── vdw_fitB.ntype
│ │ └── Wij.txt
│ ├── input
│ │ ├── (egroup.in) # Only works when ATOMIC ENERGY exists in the MOVEMENT
│ │ └── *feature.in
│ └── (output)
│ └── grid* # Used when feature 1, 2 is applied
│
└── model_record
│ ├── epoch_train.dat # Training error for each epoch
│ ├── epoch_valid.dat # Validation error for each epoch
│ ├── iter_train.dat # Training error for each batch
│ ├── iter_valid.dat # Validation error for each batch
│ ├── nn_model.ckpt # Model file
│ └── scaler.pkl # Extracting scaler values of the model
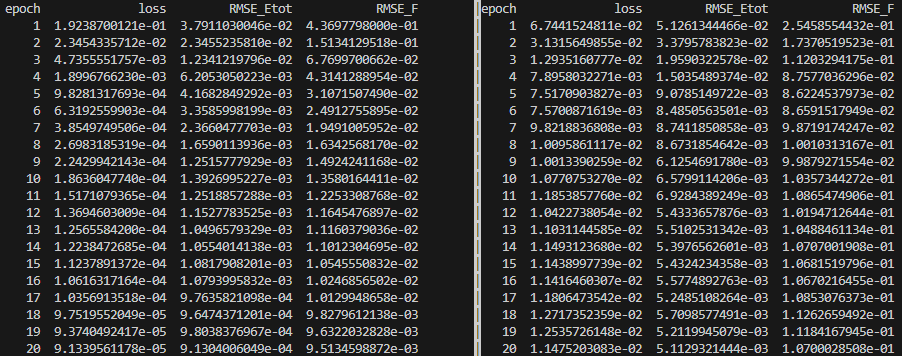
losscorresponds to the total training error.RMSE_Etotcorresponds to the energy error during training.RMSE_Fcorresponds to the force error during training.
3. Validation/Testing
After training is complete, you can validate or test the model to assess its fitting performance.
Create a new directory (e.g., MD) and copy another MOVEMENT file into this directory. Then, set the test_movement_file and test_dir_name parameters in the .json file, and add the model_load_file parameter.
Relevant Input Example:
"test_movement_file":["./MD/MOVEMENT"],
"test_dir_name":"test_dir",
"model_load_file":"./model_record/nn_model.ckpt",
Example of Running Validation:
Change train to test in PWMLFF train nn_ec.json:
PWMLFF test nn_ec.json
After running the program, validation results will be stored in the directory specified by test_dir_name.
4. LAMMPS Simulation
The generated *.ff force field file can be used for LAMMPS simulation (requires a recompiled version).
To use the force field file generated by PWMLFF, include the following in the LAMMPS input file:
pair_style pwmatmlff
pair_coeff * * 3 1 forcefield.ff 8 6 1
Here, 3 indicates the use of the Neural Network model, 1 specifies reading one force field file, forcefield.ff is the name of the PWMLFF-generated force field file, and 8, 6, 1 are the atomic numbers for O, C, and H, respectively.
Example LAMMPS input file (NVT ensemble):
units metal
boundary p p p
atom_style atomic
processors * * *
neighbor 2.0 bin
neigh_modify every 10 delay 0 check no
read_data POSCAR.lmp
pair_style pwmatmlff
pair_coeff * * 3 1 forcefield.ff 8 6 1
velocity all create 300 206952 dist gaussian
timestep 0.001
fix 1 all nvt temp 300 300 0.1
thermo_style custom step pe ke etotal temp vol press
thermo 1
dump 1 all custom 1 traj.xyz id type x y z vx vy vz fx fy fz
run 1000
5. Input File Parameter Details
{
"recover_train":false,
"work_dir":"./work_train_dir",
"reserve_work_dir": false,
"train_movement_file":["./PWdata/MOVEMENT"],
"forcefield_name": "forcefield.ff",
"forcefield_dir": "forcefield",
"test_movement_file":["./MD/MOVEMENT"],
"test_dir_name":"test_dir",
"train_valid_ratio":0.8,
"model_type": "NN",
"atom_type":[8,6,1],
"feature_type":[7],
"max_neigh_num":100,
"model":{
"fitting_net": {
"network_size": [15, 15, 1]
},
"descriptor": {
"Rmax":6.0,
"Rmin":0.5,
"1":{
"numOf2bfeat": 24,
"iflag_grid": 3,
"fact_base": 0.2,
"dR1": 0.5,
"iflag_ftype": 3
},
"2":{
"numOf3bfeat1" : 3,
"numOf3bfeat2" : 3,
"iflag_grid" : 3,
"fact_base" : 0.2,
"dR1" : 0.5,
"dR2" : 0.5,
"iflag_ftype" : 3
},
"3":{
"n2b": 6,
"w": [1.0, 1.5, 2.0]
},
"4":{
"n3b": 20,
"zeta": 2.0,
"w": [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0]
},
"5":{
"n_MTP_line":5
},
"6":{
"J":3.0,
"n_w_line":2,
"w1":[0.9, 0.1, 0.8, 0.2, 0.7, 0.3, 0.6, 0.4],
"w2":[0.1, 0.9, 0.2, 0.8, 0.3, 0.7, 0.3, 0.6]
},
"7":{
"M":25,
"M2":4,
"weight_r":1.0
},
"8": {
"M":8,
"weight_r":1.0,
"w":[1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5]
}
}
},
"optimizer":{
"optimizer":"LKF",
"block_size":5120,
"kalman_lambda":0.98,
"kalman_nue":0.99870,
"nselect":24,
"groupsize":6,
"batch_size": 1,
"epochs":5,
"start_epoch":1,
"print_freq":10,
"train_energy":true,
"train_force":true,
"train_ei":false,
"train_virial":false,
"train_egroup":false,
"pre_fac_force":2.0,
"pre_fac_etot":1.0,
"pre_fac_ei":1.0,
"pre_fac_virial":1.0,
"pre_fac_egroup":0.1
}
}
recover_train: Whether to continue training from the last interruption/completion. If set totrue, the program will resume training from the last interruption/completion point using the defaultmodel_load_pathandmodel_name. See Parameter Details for more information.work_dir: Directory for storing intermediate files during training. This directory is automatically deleted after training completes. Ifreserve_work_diris set totrue, the directory will not be deleted after training.train_movement_file: Name of theMOVEMENTfile(s). Multiple files can be specified. Adjust according to your needs.forcefield_name: Name of the generated force field file. This is optional.forcefield_dir: Directory for storing the generated force field file. This is optional.test_movement_file:MOVEMENTfile used for validating the model after training is complete. (Details on Validation/Testing)test_dir_name: Directory for storing theMOVEMENTfile used for model validation after training.model_type: Model type being used for training. For other model types and parameter configurations, refer to Parameter Details.atom_type: Atomic types, where 8, 6, and 1 correspond to the atomic numbers of O, C, and H, respectively.max_neigh_num: Maximum number of neighboring atoms.model: Model parameters. For specific parameter configurations, refer to Parameter Details.Rmax: Maximum cutoff radius for features.Rmin: Minimum cutoff radius for features.feature_type: Type of feature, where 7 corresponds to DP-Chebyshev features. See Feature Types for details.optimizer: Optimizer parameters, withLKFrecommended. Generally, for large systems and networks, using theLKFoptimizer can speed up training. For other optimizers and additional parameter configurations, refer to Parameter Details.epochs: Number of training iterations. Adjust based on the total number of images in theMOVEMENTfile. For fewer images, you may increase this number, e.g., to 30.